进销存英语怎么说?库存管理英文术语详解及ERP系统应用场景介绍
-
来源:建米软件
-
2025-06-12 22:51:35
-
Understanding Inventory Management: The English Terminology and ERP Integration
Inventory management is a critical aspect of any business, ensuring that the right products are available at the right time and in the right quantity. In the global business landscape, effective inventory management is not just about tracking stock levels but also about optimizing costs and improving customer satisfaction. This article delves into the English terminology used in inventory management, explores the core objectives, and introduces the application scenarios of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems in this domain.
1. Key Terminology in Inventory Management
Inventory management encompasses a variety of terms that are essential for understanding the process. Here are some of the most important ones:
Inventory: This refers to the goods and materials that a business holds for sale, use, or production. It includes raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods.
Inventory Turnover: This metric measures how quickly a company sells its inventory. A high turnover rate indicates efficient inventory management, while a low rate may suggest overstocking or slow sales.
Inventory Accuracy: This term refers to the degree to which the physical inventory matches the recorded inventory. High accuracy is crucial for making informed business decisions.
Just-In-Time (JIT): A inventory management strategy where inventory is received and used as it is needed, reducing storage costs and minimizing waste.
Reorder Point: The level of inventory at which a new order should be placed to avoid stockouts. It is calculated based on lead time, demand, and safety stock.
2. Core Objectives of Inventory Management
The primary goals of inventory management are to:
Optimize Stock Levels: Ensuring that the right amount of inventory is on hand to meet customer demand without incurring excessive holding costs.
Minimize Costs: Reducing costs associated with inventory, such as storage, handling, and obsolescence.
Improve Customer Satisfaction: Ensuring that products are available when customers need them, leading to higher satisfaction and repeat business.
Enhance Decision-Making: Providing accurate and timely information to support strategic and operational decisions.
Streamline Operations: Improving efficiency in the supply chain by reducing lead times and improving inventory turnover.
3. Implementation of Inventory Management Systems
Implementing an effective inventory management system involves several steps:
Assessment of Current Processes: Understanding the existing inventory management practices to identify areas for improvement.
Selection of the Right System: Choosing an inventory management system that aligns with the business's needs and can integrate with other systems, such as ERP.
Data Migration: Transferring existing inventory data to the new system, ensuring accuracy and completeness.
Training and Support: Providing training to staff on how to use the new system and offering ongoing support to address any issues.
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement: Regularly reviewing inventory levels and performance metrics to identify areas for further optimization.
4. Challenges and Solutions in Inventory Management
Managing inventory effectively comes with its own set of challenges:
Challenge: Stockouts
Solution: Implementing a robust reorder point system and maintaining a safety stock to mitigate the risk of stockouts.
Challenge: Overstocking
Solution: Using inventory turnover ratios and demand forecasting to avoid overstocking and tie up capital unnecessarily.
Challenge: Data Accuracy
Solution: Regularly reconciling physical inventory with recorded inventory and using barcode scanning or RFID technology to improve accuracy.
Challenge: Integration with Other Systems
Solution: Choosing an inventory management system that can easily integrate with other business systems, such as ERP, to streamline operations.
Challenge: Market Changes
Solution: Staying informed about market trends and customer preferences to adjust inventory levels and product offerings accordingly.
【PART1-CHECK】序号一-四连续
【PART2-NEW DIRECTIONS】5. The Role of Technology in Inventory Management
In today's digital age, technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing inventory management. Here are some key technological advancements that are reshaping the landscape:
Barcode and RFID Technology: These technologies have revolutionized inventory tracking by providing a fast and accurate way to identify and manage products. They reduce errors and save time, leading to improved efficiency.
Cloud-Based Inventory Management Systems: Cloud technology allows businesses to access their inventory data from anywhere, at any time. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for companies with multiple locations or those that operate in remote areas.
AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to predict future inventory needs, optimize stock levels, and identify trends. This helps businesses make informed decisions and reduce costs.
Blockchain for Traceability: Blockchain technology can be used to track the movement of goods throughout the supply chain, ensuring transparency and reducing the risk of fraud.
6. The Impact of E-commerce on Inventory ManagementThe rise of e-commerce has brought about significant changes in the way businesses manage their inventory. Here's how e-commerce is reshaping inventory management:
Real-Time Inventory Updates: E-commerce platforms require real-time inventory updates to ensure that customers see accurate stock levels. This requires businesses to implement efficient inventory management systems.
Increased Demand Variability: E-commerce can lead to increased demand variability, as products can become popular or go out of stock quickly. Businesses need to be agile and responsive to these changes.
Focus on Customer Experience: E-commerce emphasizes the importance of customer satisfaction. Efficient inventory management ensures that products are available when customers need them, leading to higher customer satisfaction and repeat business.
Integration with Third-Party Logistics (3PL): Many e-commerce businesses rely on third-party logistics providers to manage their inventory. Integrating with 3PLs can streamline operations and improve efficiency.
7. The Importance of Collaboration in Inventory Management
Effective inventory management requires collaboration across different departments within a business. Here's why collaboration is crucial:Supply Chain Collaboration: Collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers is essential for ensuring that inventory is available when needed. This requires open communication and shared goals.
Cross-Functional Teams: Cross-functional teams, such as those involving sales, marketing, and operations, can work together to identify inventory trends and make informed decisions.
Vendor Relationships: Building strong relationships with vendors can help businesses negotiate better pricing, improve lead times, and ensure a steady supply of inventory.
Customer Feedback: Incorporating customer feedback into inventory management decisions can help businesses identify trends and adjust their inventory levels accordingly.
8. The Future of Inventory ManagementThe future of inventory management is likely to be shaped by several emerging trends:
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices can be used to monitor inventory levels in real-time, providing businesses with valuable data to optimize their inventory management.
Augmented Reality (AR): AR can be used to provide employees with real-time information about inventory levels and product locations, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
Blockchain for Enhanced Transparency: Blockchain technology can be further integrated into inventory management to provide enhanced transparency and reduce the risk of fraud.
Artificial Intelligence for Predictive Analytics: AI will continue to play a significant role in inventory management, providing businesses with predictive analytics to optimize their inventory levels and reduce costs.
常见用户关注的问题:常见用户关注的问题:
一、标题翻译及场景大白话
标题翻译为:“Common User Concerns:”
大白话:这个标题的意思是“用户们经常关心的问题:”,通常用于列出一些用户在使用某个产品或服务时,经常遇到并询问的问题。
二、库存管理英文术语详解
库存管理(Inventory Management)是企业管理中非常重要的一环,涉及到多个英文术语。以下是一些常见的英文术语及其解释:
1. Inventory:库存,指企业拥有的商品、原材料、在制品和成品等。
2. Stock Keeping Unit (SKU):库存单位,是库存管理中最小的计量单位,通常与商品条码相对应。
3. Inventory Turnover:库存周转率,指企业在一定时期内销售商品的平均次数,是衡量库存管理效率的重要指标。
4. Just-In-Time (JIT):准时制,是一种库存管理方法,通过减少库存量,降低库存成本,提高生产效率。
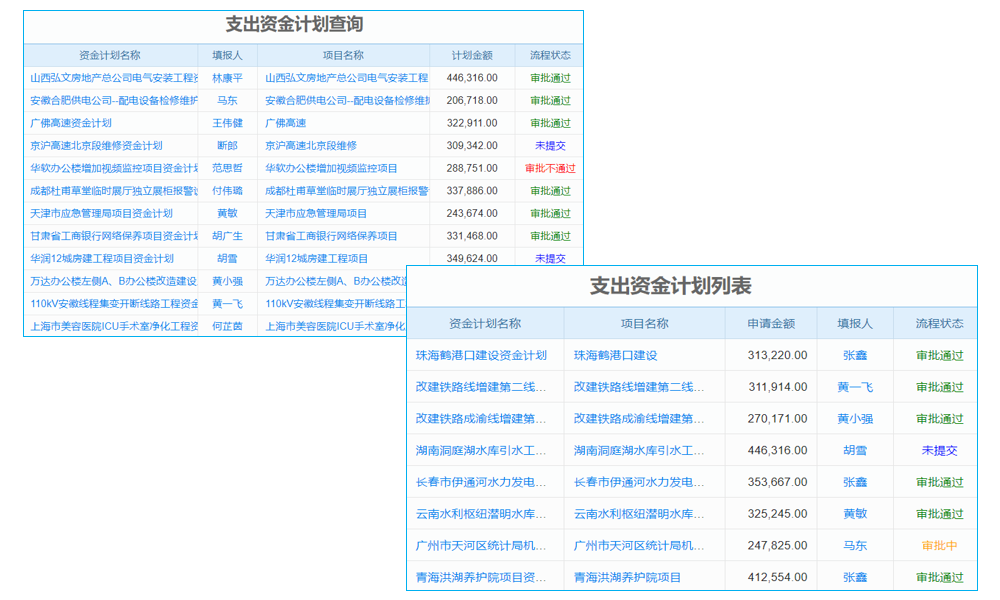
三、ERP系统应用场景介绍
ERP(Enterprise Resource Planning)系统是一种集成企业管理软件,将企业的各个部门、业务流程和资源整合在一起。以下是一些ERP系统的应用场景:
1. 供应链管理:ERP系统可以帮助企业优化供应链,提高采购、生产、销售等环节的效率。
2. 财务管理:ERP系统可以提供全面的财务报表和分析,帮助企业进行财务决策。
3. 人力资源管理:ERP系统可以帮助企业进行员工招聘、培训、薪酬管理等人力资源管理工作。
4. 客户关系管理:ERP系统可以记录客户信息,帮助企业进行客户关系维护和销售管理。
四、必应搜索相关问答
1. 什么是库存周转率?
库存周转率是指企业在一定时期内销售商品的平均次数,是衡量库存管理效率的重要指标。计算公式为:库存周转率 = 销售成本 / 平均库存。
2. 什么是JIT库存管理?
JIT(Just-In-Time)库存管理是一种库存管理方法,通过减少库存量,降低库存成本,提高生产效率。其核心思想是“按需生产”,即在需要时才进行采购和生产。
3. ERP系统有哪些功能?
ERP系统具有多种功能,包括供应链管理、财务管理、人力资源管理、客户关系管理等。它可以帮助企业整合各个部门、业务流程和资源,提高管理效率。
4. 如何提高库存周转率?
提高库存周转率可以通过以下方法实现:优化供应链,减少库存积压;提高销售效率,增加销售量;合理规划生产计划,减少生产周期。
- 上一篇:进销存结存设置方法及注意事项详解
- 下一篇:返回列表
预约免费体验 让管理无忧
微信咨询


添加专属销售顾问
扫码获取一对一服务